A Rainforest Walk
Plant activities
1. Strangler Fig - Ficus thonningii

This tree begins its life high up on a host tree in the canopy. It sends down roots that twist around the host's trunk before reaching the ground up to 40m below.
The strangler's roots thicken and grow to eventually enclose and kill the supporting host tree.
How could the seed in these figs find its way to the top of tall rainforest trees?
____________________________________
What is the advantage of starting life high up in the rainforest canopy?
_____________________________________
How does the shape of the roots indicate the tree may be a ‘strangler’?
_____________________________________
What is unusual about where the roots are growing on this plant?
_____________________________________
What does this tell us about the air in the tropics?
_____________________________________
List some of the ways the strangler could kill its host.
______________________________________
2. Mosses and Lichens - Epiphytes
Lichens and mosses cover the trunk of this tree.
This is common in rainforest. Plants that grow high up on their hosts without harming them are called epiphytes.
Epiphytes do not grow in the soil.
What problems does this create for them?
__________________________________________
What is the advantage of being an epiphyte?
__________________________________________
3. Canopy Layer
Spreading branches and the dense leaf growth of large trees forms the canopy or roof of the rainforest. The canopy controls the environment for living things below.
When you moved from the open-lawn area to the middle of this stand of trees, by station 4, what changes did you notice in the following factors at ground level?
Sunlight ____________________ Humidity ____________________
Temperature ________________ Wind _______________________
Where doesn’t the lawn grow around here? Why? __________________________________
4. Upper Canopy - Ficus macrophylla
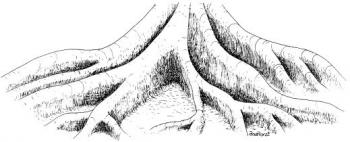
Rainforest soils are wet and shallow, with nutrients near the surface.
List two ways the large buttress roots help trees growing such soils.
1. ___________________________________
2. _________________________________
What happens to the soil when large numbers of canopy trees are removed?
_______________________________________________________
What happens to the understorey plants if the canopy trees are removed?
_______________________________________________________
5. Emergents
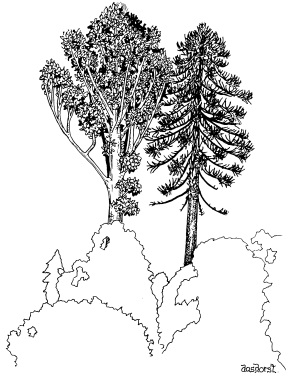
Sometimes the canopy has taller trees "emerging" above it.
Two such emergents are the Kauri Pine and Bunya Pine.
Describe how the shapes of the Kauri Pine in the foreground and the Bunya Pine in the background are well suited to growing above the canopy.
____________________________________
____________________________________
Why are emergent trees often logged?
____________________________________
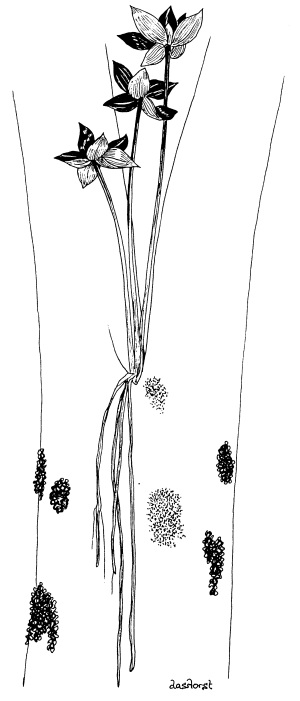
6. Molineria capitulata
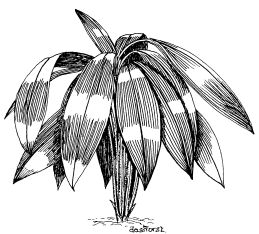
Rainforests contain 170 000 flowering plant species of which currently 60 000 are at risk.
Flowers of the rainforest come in all colours, shapes and sizes.
Take time to look at the many examples we have collected in the Conservatory.
Where are the flowers on this plant? _________________________________________
Why is this position unusual? _______________________________________________
What sort of animals might visit flowers in this position? ___________________________
7. Giant Fern - Angiopteris evecta

Ferns are common in the rainforest. Angiopteris is an ancient fern with ancestors going all the way back to when
Where could other Australian rainforest plants have come from?
__________________________
(Hint: Use the plant labels.)
Look for brown edges on the underside of the leaves. This is the reproductive part of ferns.
Do they contain spores or seeds? ______________
8. Rose Apple - Syzygium moorei

Tropical forests are being cleared at an alarming rate.
Plants are becoming extinct at a rate of over 1-2 species per day.
This
What can be done to prevent the extinction of this species?
____________________________
How can a botanic garden help?
_____________________________
9. Walking Stick Palm - (Linospadix monostachya)

This small palm was used to make strong, flexible walking sticks.
What features make it suitable for this purpose?
__________________________________
One end the walking stick had a rounded decorative hand grip carved to fit the
palm of the hand. From what part of the plant would this grip have been made?
__________________________________
10. Powderpuff Lilly-pilly - Syzygium wilsonii

In season this slender understorey shrub has crimson flower clusters that look like pom-poms. They mature into clusters of small white fruits.
Where on the plant are the flowers or fruit?
__________________________
How does this position assist the flowers to attract insects and the fruit to be spread by animals?
___________________________
Over 75% of Australian rainforest plants produce fleshy fruit.
What types of rainforest animals might eat this fruit and hence spread the seed?
11. Wild Banana - (Musa banksii)
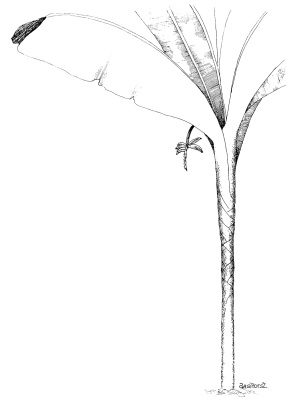
This is the most common of
What part of the plant are the small, green bananas attached to?
____________________________________
Wild rainforest banana plants have been selected and bred to produce the tasty fruit we eat.
What do you think ‘wild bananas’ would taste like?
_________________________________________
New strains of disease are capable of wiping whole crops of farm-grown bananas because they are genetically identical.
How could such ‘wild’ plants with ‘wild’ genes help overcome this problem?
________________________________________
12. Climbers - Epipremnum pinnatum
The rainforest floor beneath the upper canopy is dark. Very few plants able to grow well in the low amounts of light available.
Woody vines called lianas stretch from the forest floor to the canopy depending on trees to support them.
What is the advantage of being a climber in the rainforest?
_______________________________________________
What part of the Epipremnum is being used to hold on to the palm trunk?
_____________________________________________
How could this climber eventually harm the palm that supports it?
___________________________________________________
Find another climber nearby, what is it using to climb?
_____________________________________________
13. Leichhardt Tree - Nauclea orientalis
Aboriginal uses of this tree include: canoes, fish poisons, medicines, yellow dye and pain-killers. The bitter fruit can also be eaten.
Plants like this make rainforest a home to many millions of indigenous people.
How are these people affected when rainforest is cleared?
How might the bark have been used by traditional Aboriginal people?
___________________________________________________
14. Tree Fern - Cyathea

The design and structure of Cyathea leaves enable them to grow in areas of low light intensity on the forest floor.
Explain how the following features assist the fern in gaining light.
The size of the leaves.
________________________________
Finely divided leaves.
________________________________
The way the leaves are displayed.
________________________________
15. Bird's Nest Fern - Asplenium nidus
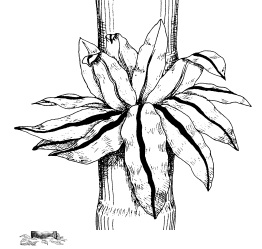
What part of the fern looks like a bird’s nest?
______________________
Carefully feel the base. How does it help the plant?
__________________________________________
How does the display of the leaves help the plant obtain water and nutrients?
In rainforests plants and animals often help each other. This is called mutualism. Epiphytes often provide a home for ants.
How might the ant home help the epiphyte?
_____________________________________________
16. Leaf litter

Rainforests grow rapidly and produce large amounts of leaf litter that is quickly recycled once on the forest floor.
Carefully lift up the top layer of the leaf litter and describe what is happening to the material below.
___________________________________________________________________________
What conditions and living things in the rainforest cause this rapid decay?
Conditions __________________________
Living things __________________________
Why is this process important to the growth of rainforest plants?
___________________________________________________________________________
17. Stilt roots - Pandanus oblatus

Note the roots of this plant.
Explain why they are called ‘stilt’ roots.
___________________________________
Pandanus often lives near swamps and creeks.
List two ways in which the stilt roots would help pandanus survive in these regions.
________________________________________
________________________________________
18. Elephant Ears - Alocasia macrorrhiza
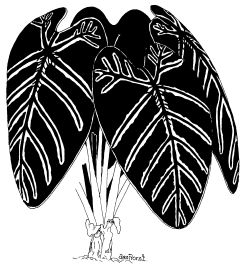
Rainfall in tropical areas is over 1500mm a year. Downpours and constant moisture mean plants have to shed water quickly from their leaves before they are weighed down.
Constant moisture also invites smaller plants to grow on the leaf surface. A photograph, on the wall at the end of the conservatory, demonstrates this well.
By looking and touching the leaf, find three features that protect it from too much moisture.
1. ___________________________________
2. ___________________________________
3. ___________________________________
19. Native Ginger - Alpinia caerulea

Rainforests provide a wealth of food for the world. Common fruits such as bananas, nuts like macadamias and staples like tea, coffee, rice and cocoa, all originate from rainforests.
This plant is a relative of the common ginger. It is the hardiest of the native gingers. Aboriginal people ate its root tips.
What other part of the plant can you see that may have provided a ginger taste when eaten?
____________________
Draw a sketch of what you see here.
20. Fan Palm - Licuala speciosa

How is this leaf designed to overcome a lack of light?
____________________________________
Feel the thickness and note the size of the leaf. What prevents it from flopping down ?
____________________________________
What other part of this plant is green in order to absorb sunlight? _______________________